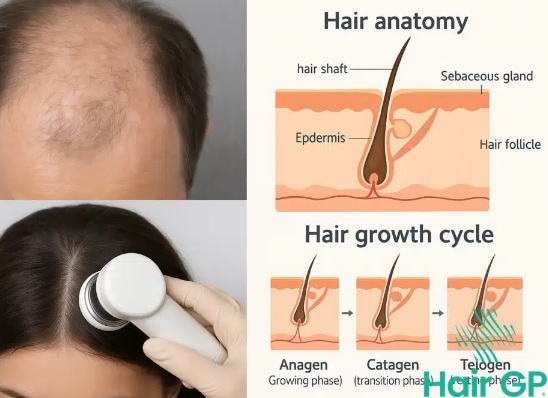
Hair loss is a common concern that affects millions of individuals worldwide. Understanding how it is diagnosed can empower you to take action and seek appropriate solutions. In this blog post, we’ll outline the critical steps involved in diagnosing hair loss.
1. Recognizing the Symptoms
The first step in diagnosing hair loss is to recognize the symptoms. Hair thinning, excessive shedding, and bald patches are some of the most common indicators. It’s essential to observe the pattern of hair loss, as different types may suggest various underlying causes.
For instance, conditions like male or female pattern baldness typically lead to a gradual thinning over time, while conditions like alopecia areata result in sudden patches of baldness. Keeping a detailed account of when you started noticing changes and any accompanying symptoms can significantly aid in your diagnosis.
-
- Note when the hair loss began.
-
- Document the exact areas affected.
-
- Pay attention to any accompanying symptoms like itching or redness.
-
- Track any lifestyle changes (diet, stress) around the time of hair loss.
2. Medical History Evaluation
After identifying symptoms, the next step is a thorough evaluation of your medical history. A healthcare provider will likely ask about any family history of hair loss, existing medical conditions, and medications you might be taking. Understanding your background can reveal hereditary factors and potential triggers that contribute to hair loss.
Sometimes, hair loss can be linked to hormonal imbalances, nutrient deficiencies, or autoimmune diseases. An accurate diagnosis often requires considering these medical factors. For example, thyroid issues can significantly impact hair health, making it vital to share your complete health narrative with your healthcare provider.
-
- Be prepared to discuss family history of hair loss.
-
- List all medications you are currently taking.
-
- Disclose any medical conditions you have.
-
- Keep track of changes in your wellness, like significant stress or recent illnesses.
3. Diagnostic Tests and Physical Examination
Once your medical history is assessed, the next phase may involve physical examination and diagnostic testing. A dermatologist may perform a thorough scalp examination to determine hair density and the health of your follicles. They might pull on some hairs to evaluate shedding patterns.
In some cases, blood tests or a scalp biopsy may be recommended. Blood tests can check for hormonal levels, nutrient deficiencies, or autoimmune diseases, while a biopsy of the scalp can provide further insights into the type of hair loss and its potential causes. This diagnostic phase is crucial in determining the best course of treatment.
-
- Inquire if a scalp biopsy is necessary.
-
- Discuss potential blood tests that may be ordered.
-
- Prepare for a physical examination by washing your hair 24 hours prior.
-
- Be open to following up with additional tests if initial ones suggest underlying issues.
4. Exploring Treatment Options
Once a hair loss diagnosis is confirmed, the next important step is exploring treatment options. Treatments can vary greatly based on the underlying cause. For example, if hair loss is due to a deficiency in iron or vitamin D, supplementation may be recommended.
Other common treatments include topical solutions like minoxidil or prescription medications such as finasteride. In more severe cases, treatments like laser therapy or hair transplants may be considered. Each option comes with its own benefits, risks, and timelines, so it’s crucial to have a thorough discussion with your healthcare provider about what’s suitable for you.
-
- List all treatment options you’re considering.
-
- Consult with a specialist to determine suitability for each option.
-
- Be realistic about timelines and outcomes.
-
- Follow a consistent routine if prescribed treatments.
5. Emotional and Psychological Impact
Beyond the physical aspects, hair loss can have emotional and psychological implications. Many individuals experience feelings of embarrassment, anxiety, or a decrease in self-esteem when dealing with hair loss. Acknowledging these feelings is important as it helps develop a holistic approach to treatment.
Consider seeking support from counseling or support groups where you can share experiences and coping strategies. Engaging with a community can bolster your resilience and provide valuable insight from others in similar situations. Additionally, discussing these feelings with your healthcare provider can ensure that mental health factors are addressed alongside physical symptoms.
-
- Be open about your feelings regarding hair loss.
-
- Seek support from friends or family.
-
- Consider professional counseling if feelings become overwhelming.
-
- Join a support group for shared experiences and strategies.
In conclusion, diagnosing hair loss involves recognizing symptoms, evaluating your medical history, undergoing diagnostic tests, and exploring treatment options. Don’t hesitate to reach out to a healthcare professional to discuss your concerns and take the first step towards effective management. Being proactive can lead to positive changes and improvement in both your hair and overall well-being.