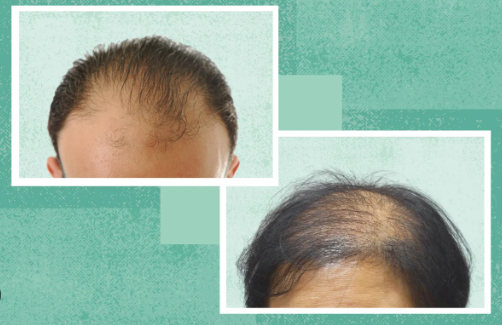
Androgenetic alopecia, commonly known as male or female pattern baldness, is a widespread condition affecting millions globally. Understanding its causes, symptoms, and treatment options can empower individuals suffering from hair loss to take proactive steps toward managing their condition.
1. Understanding Androgenetic Alopecia
Androgenetic alopecia is primarily tied to genetics and hormonal changes. It occurs when hair follicles shrink since they are sensitive to a derivative of testosterone called dihydrotestosterone (DHT). This shrinking can lead to thinning hair and eventual baldness, typically starting from the crown or the front of the scalp in men, while women usually experience wider partings and overall thinning.
The condition affects both men and women, albeit differently. While it follows a more defined pattern in men—often referred to as the Norwood scale—in women, the patterning can be less uniform, which may make it harder to diagnose early on. Surprisingly, around 50% of men over 50 experience some form of hair loss due to this condition, making awareness and early intervention crucial.
-
- Understand your family history regarding hair loss.
-
- Consult a dermatologist for an initial assessment.
-
- Be aware of early symptoms like thinning hairlines or widening parts.
-
- Learn the difference between male and female pattern baldness.
2. Treatment Options
Several treatments are available for androgenetic alopecia, ranging from topical solutions to surgical options. Minoxidil (Rogaine) and finasteride (Propecia) are the most commonly used medications. Minoxidil, available over the counter, can stimulate hair regrowth in some individuals, though results may vary widely. Finasteride, a prescription medication that reduces DHT levels, can be more effective but comes with potential side effects.
In addition to pharmaceutical interventions, surgical options such as hair transplants are becoming increasingly popular. These procedures involve taking hair follicles from a dense area and implanting them in balding spots. It’s worth noting that surgical options typically work best when the individual has a sufficient amount of donor hair, so early consultation is vital.
-
- Consider trying minoxidil for at least six months before deciding if it’s effective.
-
- Discuss the potential side effects of finasteride with your doctor.
-
- Investigate hair transplant options if you’re a candidate.
-
- Stay informed about non-surgical advancements, like laser therapy.
3. Lifestyle Factors That Influence Hair Health
While androgenetic alopecia has a genetic basis, certain lifestyle factors can exacerbate the condition or support hair health. A balanced diet rich in vitamins and minerals plays a critical role in maintaining hair strength. Key nutrients like biotin, zinc, and iron are particularly beneficial for hair growth, as deficiencies in these areas can lead to increased hair loss.
Moreover, stress management is crucial, as chronic stress can trigger or worsen hair loss. Engaging in regular physical activity, practicing mindfulness, or incorporating relaxation techniques into your daily routine can prove beneficial not just for your mental health but also for your hair. Remember, maintaining overall health contributes significantly to the health of your hair.
-
- Include leafy greens, fish, and nuts in your diet for hair support.
-
- Stay hydrated; aim for at least eight glasses of water a day.
-
- Practice stress management techniques like yoga or meditation.
-
- Limit harmful hair care practices, like excessive heat styling.
In conclusion, while androgenetic alopecia can be distressing, understanding it fully opens the door to effective treatment options and lifestyle changes. If you suspect you’re experiencing hair loss, don’t hesitate to consult a healthcare professional to explore your options and take the first step towards hair health. Remember, early intervention is often the key to managing this condition successfully.